The FDM technology, also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), falls under the material extrusion type of 3D printing technology. It is the most widely used 3D printing technology across the world.
FDM 3D printing uses thermoplastic polymers like PLA, ABS, PETG, TPU, etc. in a filament (wire) form that is extruded and deposited in the shape of the final object as required. The printing happens in a layer-by-layer form.
Popularly there are two types of FDM 3D printers, namely Cartesian and Delta 3D printers. Both of these types have different advantages and limitations.

3D Printing Shops 3D Printing Service FDM – Fused Deposition Modeling
3D Printing Shops 3D Printing Service FDM – Fused Deposition Modeling
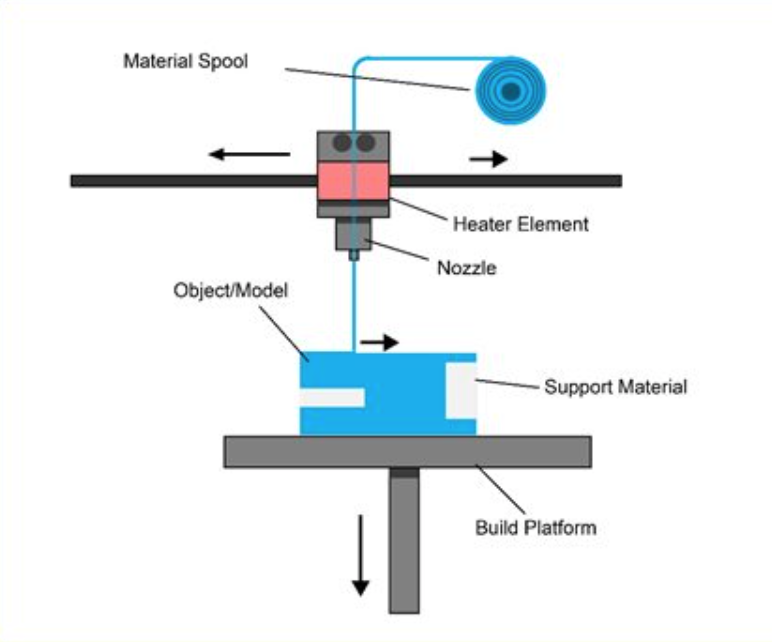
COMPONENTS OF AN FDM 3D PRINTER
Extrusion Head: It is also known as an extruder, it is one of the most important components of an FDM 3D printer. The extruder is an assembly of three sub-components like an extrusion system, heater, and the nozzle. All three sub-components work in tandem with the extruder.
The extrusion system pulls the filament into the heater, which heats the filament, and the nozzle then deposits the heated material onto the build platform.
Filament: This is the thermoplastic material in a wire/filament form wound around a spool.
Build Platform: It is also called Build plate or Bed. The material is deposited onto the build platform. Depending on the 3D printer, this build platform can either be cold or hot.
WORKING OF AN FDM 3D PRINTER
The FDM 3D printing process starts with the feeding of the filament into the extruder assembly through the extrusion system. The filament passes through to the heater in the extruder assembly. Here the filament is heated to a pre-defined temperature depending on the type of filament whether PLA, ABS, or PC.
Once the ideal temperature is reached, the material is then made to pass through the nozzle. The nozzle then moves according to the G-Code of the model created in the slicing software. The nizzle traces the geometry of the design.
The nozzle deposits the semi-liquid material onto the build platform and prints the cross-section of the model. One cross-sectional print refers to one layer. Once the first layer is completed, the build platform drops down by an amount equal to the layer height. The nozzle then springs into action again and it prints the second layer on top of the first layer in a similar fashion.
This process continues until the entire object is formed.
Once the 3D printing process completes, the printed object needs to be removed from the build platform. Supports, if any, also need to be removed and thus the final object is ready.
Post-processing, if needed, is then carried out on this final model



